Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that is used for protection against leakage current. it breaks the circuit and disconnects the power supply to the load when it senses the leakage current.
The principle of Earth leakage protection
The principle is the same for all types of residual current devices. It can be broken down into 3 functions:
a) Detection of leakage current.
b) Measurement
c) Tripping
Measurement of the sum of currents flowing through the conductors of a circuit Opening of the contacts of the residual current device if this vectorial sum exceeds a specific value.
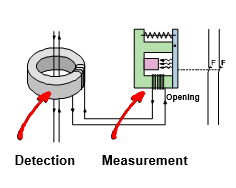
Detection
At any given point in a well insulated installation, the sum of the current flowing through all the conductors should be zero.
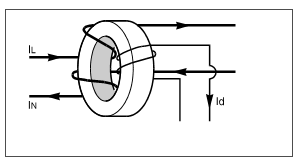
The detection is provided by a core-balance current transformer (CT) in the form of a closed ring, referred to as a toroid.
Phase(s) and neutral are used as primary windings. The direction of the winding is such that the magnetizing forces (MMF) produced by load and neutral current are in opposition. Leakage current will create an unbalanced MMF. It will create a magnetic flux in the core. A corresponding voltage will be induced. This creates current which is the representation of the leakage. current, also referred to as residual current
Measurement
It is performed by a relay which compares the electrical signal (induced current it receives) with a preset limit, the tripping threshold, also referred to as sensitivity (IDn). There are two different technologies: electromagnetic and electronic.
RCDs use only electromagnetic technology. An electromagnetic relay is composed of:
a “U” shaped electromagnet;
a permanent magnet inside the U;
a pivoting plate which bridges the open end of the U to close the magnetic circuit
a spring under tension which enables breaking of the normally closed magnetic circuit.
The coil of the U electromagnet is connected to the secondary of the toroid. When the coil is not energized (no leakage current), the attraction of the magnet holds the pivoted plate (against spring mesure). Current from the detector creates an alternating mmf that re-inforces or reduces (by half cycles) magnet attraction.

Tripping
When the residual current is sufficient to reduce the magnetic force to less than that opposed by the spring, the plate pivots and strikes a tripping mechanism.

The R.M.S value of prospective current assigned by the manufacturer, at which a RCCB can make, carry and break under specific conditions







A well-written article. Great