Protective relays form a very important part in generation, transmission & distribution of
electrical energy
Background:
Protective relays form a very important part in generation, transmission & distribution of
electrical energy
Protective relays are used for:
Protection of costly electrical equipments against faults such as:
•Overload
•Short circuit
•Earth fault
•Over/under voltage
•Safety of operating personnel
•System stability
•Restoration of electric supply with minimum down time
Development of protective relays:
Protective relays development has under gone following stages:
•Electro-mechanical relays
•Static relays
•Microprocessor based relays
•Microprocessor based relays with communication feature
FUNCTION OF PROTECTIVE RELAYS:
It must allow optimum capacity utilisation of protected equipment
- It must operate correct CB just before total capacity utilisation
- It must clear the fault before the system becomes unstable
Relays recognize and locate faults by constantly measuring electrical quantities of the system, which
are different during normal and abnormal conditions. The basic electrical quantities which may
change when a fault occurs are current, voltage, phase-angle (direction) and frequency. It is
generally necessary to provide relays responding to more than one of these conditions because for
instance, the current during fault with minimum generation may be less than the load current during
maximum generation
REQUIREMENTS TOBE FULLFILLED BY PROTECTIVE RELAYS:
Reliability
- Selectivity
- Speed
- Discrimination
- Stability
- Sensitivity
Selectivity
The ability to isolate only the defective plant from the rest of the system
- Time grading : the protection device nearest the fault trips fastest
- Amplitude of phase comparison of the currents on both side of the protected unit
- Determination of direction (of fault power flow) on both sides of protected unit
Reliability
Dependability : Measure of the certainty that the relays will operate correctly for all the
faults for which they are designed to operate.
Security: The assurance that the protection device will not trip unless there is fault on
the protected item of primary plant.
Availability: The ratio of the time that a protection device is actually serviceable to the
total time in its operation.
Electromechanical type relays:
Initially protective relays were of electromechanical design, attracted Armature or moving disc/cup type operating principal / characteristics of These relays depended on operating force of electromagnet and
Retarding force of spring.
These relays came in existence in the beginning of this century and were The only choice till 1970.
Draw back of electromechanical relays:
Slow and sluggish operation
•High error (upto ± 10%) of measurement
•High burden on CTs and PTs
•Drift in characteristics due to aging of components
•No flexibility in use hence become redundant when system grows and
fault level increases.
•Bigger dimensions
•Frequent maintenance
Static relays:
As users needs grew electromechanical relays were not found adequate and this led to
the development of static relays.
- Faster operation
- More accurate
- Low burden on CTs/PTs
- Compact size
- Less maintenance
Still static relays have not fully met ever growing needs of users
following short coming still observed in static relays:
- Not much flexibility in application
- No memory features of previous faults
- No self supervision
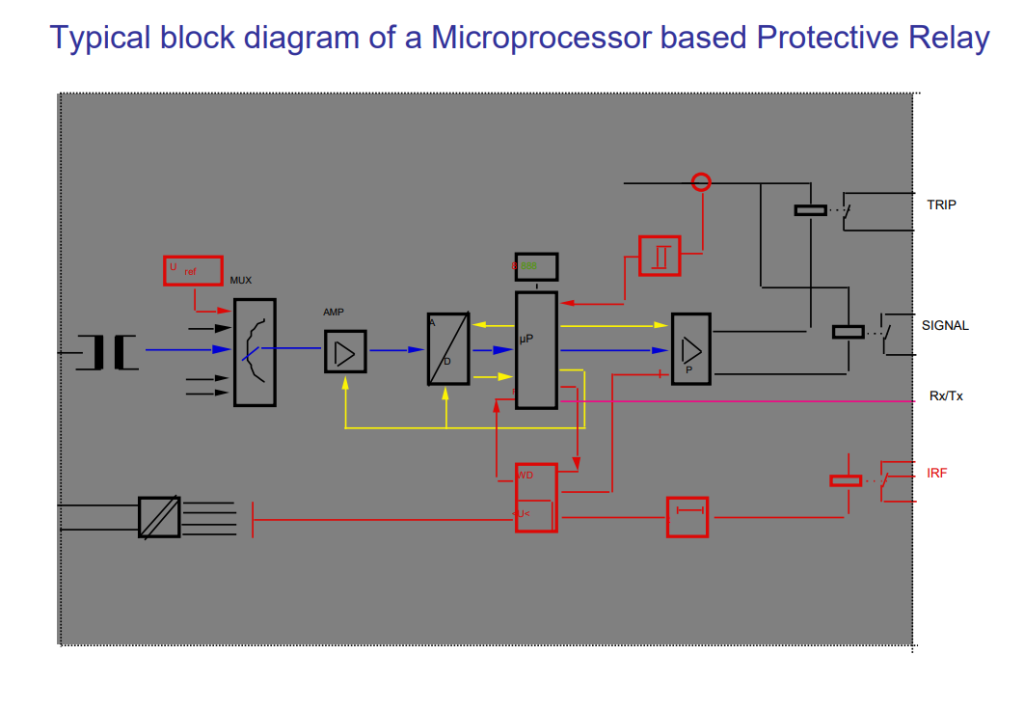
MICROPROCESSOR BASED RELAYS:
After electromechanical and static relays came the era of Microprocessor based relays.
These has been a significant development in microprocessor based Technology and it has brought revolutionary changes in all walks of Life. How can protection relay technology be behind in adopting the same.
Users now have a choice to use latest state of art microprocessor based Relays.
Advantages of microprocessor based relays:
Smaller size which allows compact switchgear cubicles and control and Relay panels which in turn results into space saving and economy.
•Digital display of all set and service values settings can be made / altered easily and accurately.
•Ample programming facilities which permit:
•Selection of required characteristics
•Exact setting from a wide range
•Output relay programming
•Blocking of selected functions depending of applications
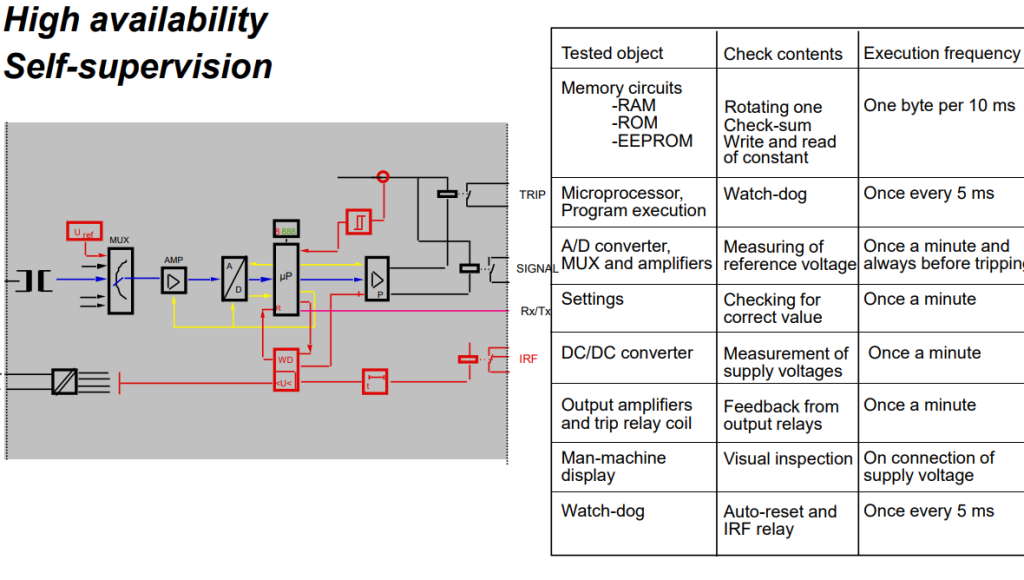
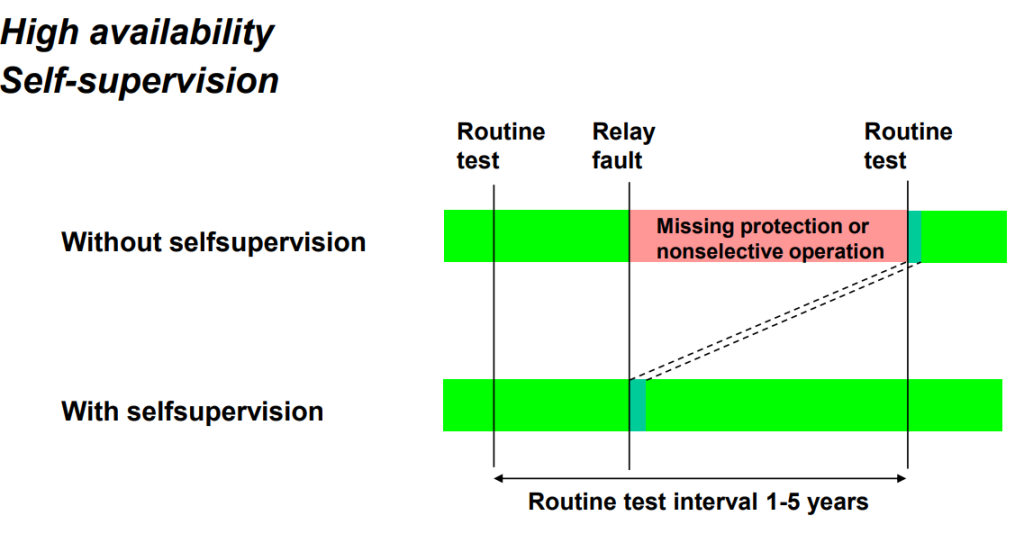
•Self supervision for healthiness of hardware & software of relay. This ensure availability of protection all the time.
•Very high accuracy of measurement.
Advantages of microprocessor based relays
Extremely low burden of current and voltage circuits which result into:
•Smaller size and economical design of CTs & PTs
•Permit larger resistance in measured circuits which in turn allow
cabling of relatively thinner cross section.
•Overall cost saving
•No variation in relay characteristics for a very long period
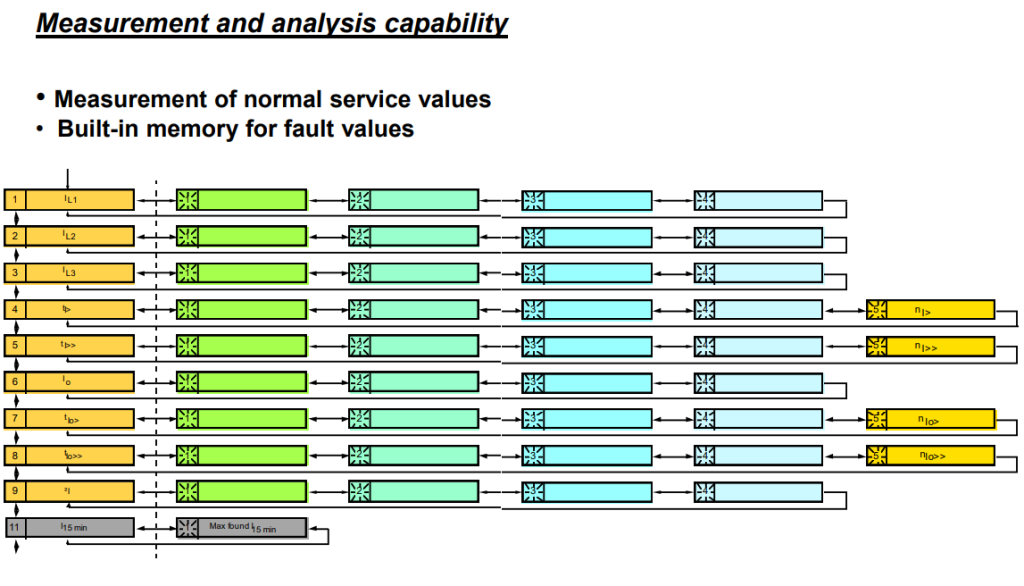
- History of previous faults enable analysis of faults which can guide for preventive
measures and planning of maintenance of primary equipment such as circuit breakers,
transformers, motor etc. and enhance life of same.
•Maintenance free design
•Simpler engineering
•Faster commissioning
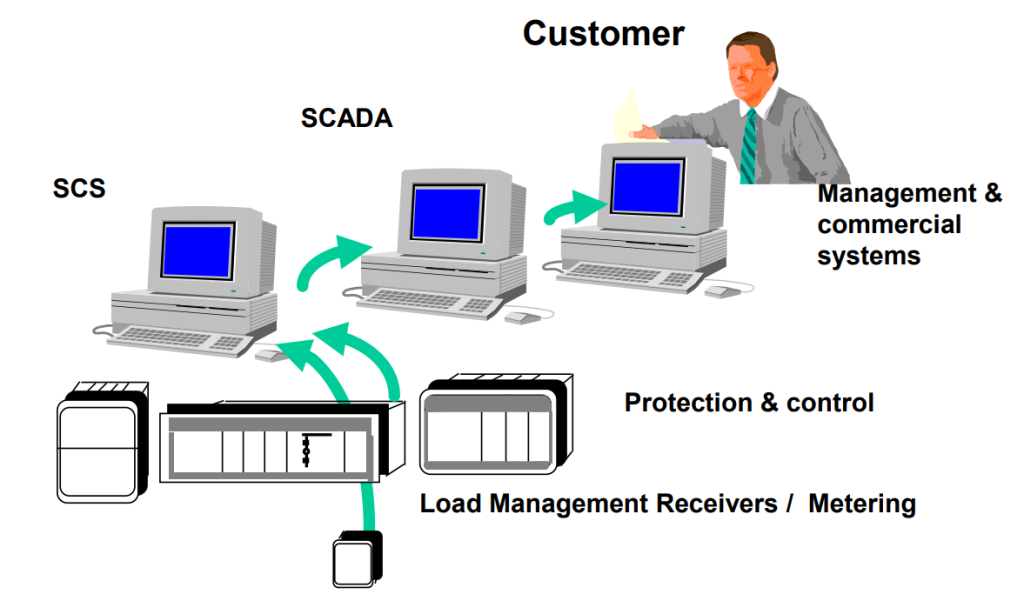
The most recent trend in microprocessor based relays
“communication capabilities”
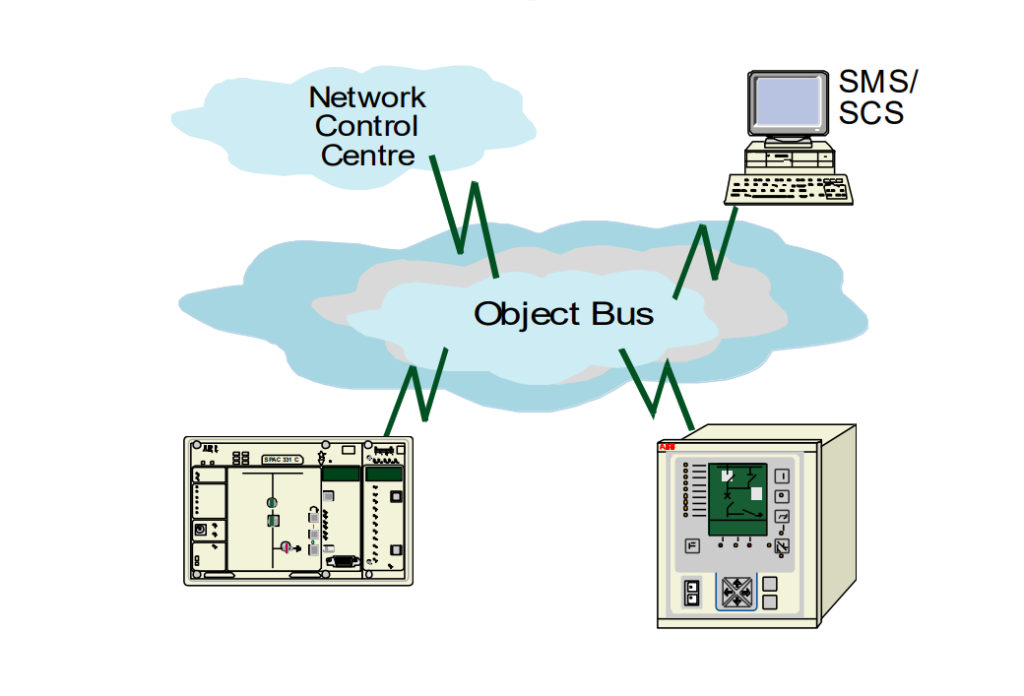
Developments are a never ending process and latest design of Microprocessors based relays are having a communication port through
Which these relays can be connected to a higher level system like:
•A monitoring system
•Data acquisition / event reporting system
•Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system
•Energy management system
Communication capability is a very powerful feature which allows user
To build in stages a “Distribution Automation System”
Such system allows most efficient and optimum utilisation of electrical
Energy and result into higher productivity and cost savings.
Salient features of communicable relays system:
•It is possible to built system step by step according to needs.
•Upgradation are very easy.
Salient features of communicable relays system:
All the relays and other system can be linked and connected to a central place for access from a remote point for:
•Reading of actual measured values
•Status information
•Recorded fault values
•Reporting of selecting events with the tagging to and event
recorder or a printer.
•Reading of setting and if necessary change.
Several sub systems can be connected using modems telephone lines / Microwave links to integrated a large area.
This gives possibilities to use a remote control system as well as operate Equipment locally.
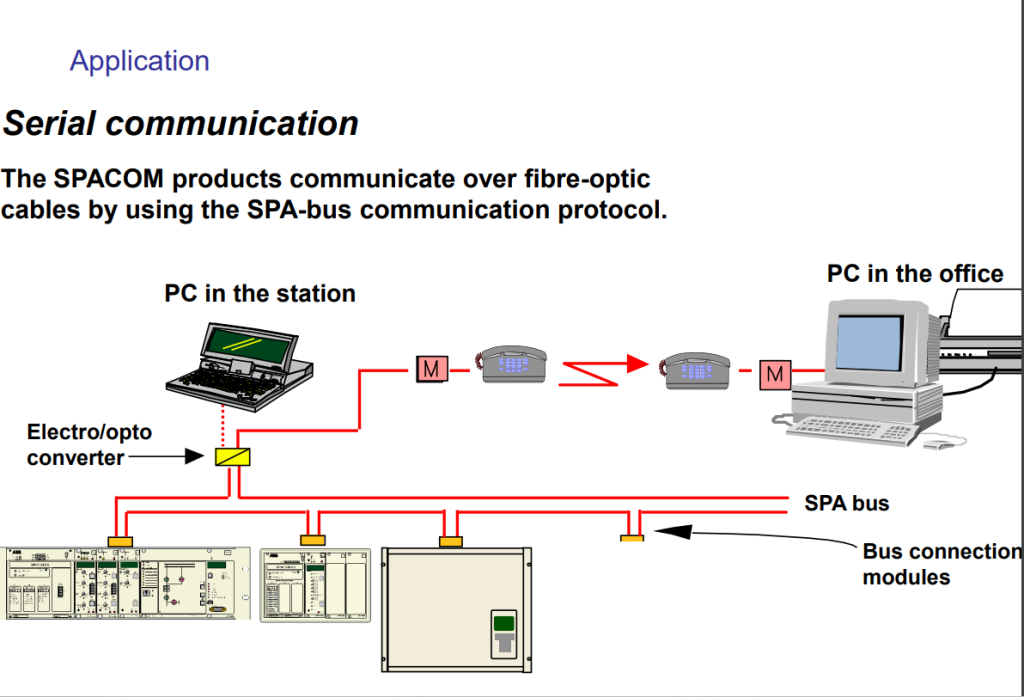


Plastic fiber connection
- Very high isolation level
- Light in the visible area
- Cables can be ordered in standard length or
made on site - Usually non-armoured cables
- Connector system “snap-in-type” HP Versatile Link
Glass fiber connection
Max. length 2 km
- Very high isolation level
- Light in the non-visible area
- Cables are ordered in standard length
- Armoured and non-armoured cables
- ST or SMA type of connectors
- Single graded index fiber 62.5/125 m or 100/140
We have competition from both organized sector and small scale
industries
- Major competitors in Electro mechanical and Static range :
- ALSTOM
- EASUN REYROLLE
- JVS
- LARSEN & TOUBRO
- ASHIDA
- JYOTI
Major competitors in Numerical range :
- ALSTOM
- MULTILIN
- SIEMENS
- LARSEN & TOUBRO
- EASUN REYROLLE
- SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC
- ASHIDA
- AVK-SEGC
Electromechanical type relays:
Initially protective relays were of electromechanical design, attracted Armature or moving disc/cup type operating principal / characteristics of These relays is depended on operating force of electromagnet and
Retarding force of spring.
These relays came in existence in the beginning of this cenury and were The only choice till 1970.
Draw back of electromechanical relays:
Slow and sluggish operation
•High error (upto ± 10%) of measurement
•High burden on cts and pts
•Drift in characteristics due to ageing of components
•No flexibility in use hence become redundant when system grows and
fault level increases.
•Bigger dimensions
•Frequent maintenance
Static relays:
As users needs grew electromechanical relays were not found adequate and this led to
the development of static relays.
•Faster operation
•More accurate
•Low burden on cts/pts
•Compact size
•Less maintenance
Still static relays have not fully met ever growing needs of users
following short coming still observed in static relays:
- Not much flexibility in application
- No memory features of previous faults
- No self supervision




